

You’ll be surprised how quickly students understand the model. During this lesson, use problems from previous grades to keep the focus on understanding tape diagrams and not on learning a new math concept. Consider doing one entire lesson on tape diagrams.
#Pictorial models in math how to
If your students are just beginning to use Eureka Math, you may wonder how to introduce them to tape diagrams if they didn’t use them in previous years. You can introduce students to tape diagrams at any time. Students use this drawing to write an equation to find the sum of each section. The last section of the top tape shows the current age difference, and both tapes together represent the total. The next section represents the daughter’s age now. The first section of each tape represents 5 years from now. This is a good example of how a tape diagram helps students organize information. The difference in their present age is 24 years. They may also work backward, subtracting the 8 hours inside the tape from the 12 total hours, and then divide the 4 hours equally among the four sections to see that each represents 1 hour.įinally, let’s look at an Algebra I problem.įive years from now, the sum of the ages of a woman and her daughter will be 40 years. Students can use a tape diagram to help write an equation such as 4(x + 2) = 12. In this case, the tape diagram shows the 4 days of practice, each with an unknown morning practice time, and 2 hours of practice in the evening. If Jenny swims 12 hours per week, how long does she swim each morning? The team swims in the morning and then again for 2 hours in the evening. Jenny is on the local swim team for the summer and has swim practice four days per week. Next, let’s look at an example of an algebraic problem from Grade 7. The drawing makes meaning of division problems clear in a way that inverting and multiplying does not. Then each half liter is partitioned to represent the amount each student gets. That rectangle is partitioned to show half liters. A larger rectangle represents a whole liter. Notice how the tape diagram represents the problem. How many liters of juice does each student get? She distributes it equally to 6 students in her tutoring group. Let’s look at how students can use tape diagrams to help them make sense of those concepts.įirst, we’ll see how students can use the tape diagram to understand operations with fractions in this example from Grade 5. What once helped with basic whole number arithmetic in primary grades extends to fractions in intermediate grades and even algebra in middle and high school.
When students encounter new challenges, the tape diagram can be a familiar place to start. Tape diagrams are useful at all grade levels. Once students know how to draw tape diagrams, they can use them to make sense of many mathematical relationships. This activity lays the foundation for the Grade 2 example, in which they start to explore equal parts. Students begin to realize how the two parts come together to make a whole-the box gathers all the dots into one group they do not appear simply as 13 discrete objects. When you draw rectangles around the dots representing the addends and indicate the sum with a question mark, you’ve made a tape diagram that reinforces the part–whole nature of the quantities.
Students can likely represent 6 + 7 by drawing dots.
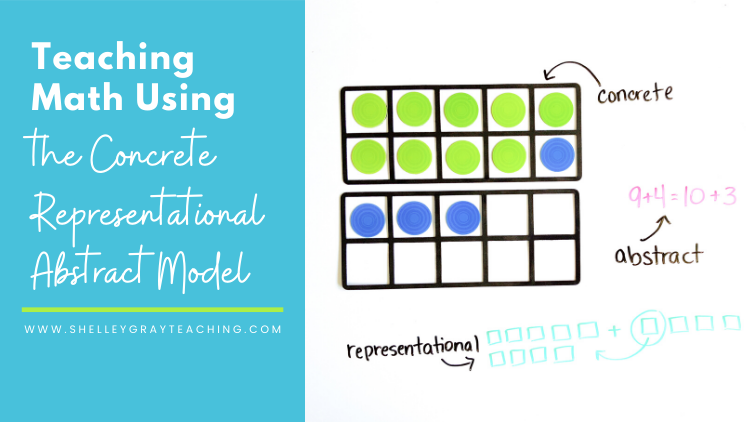
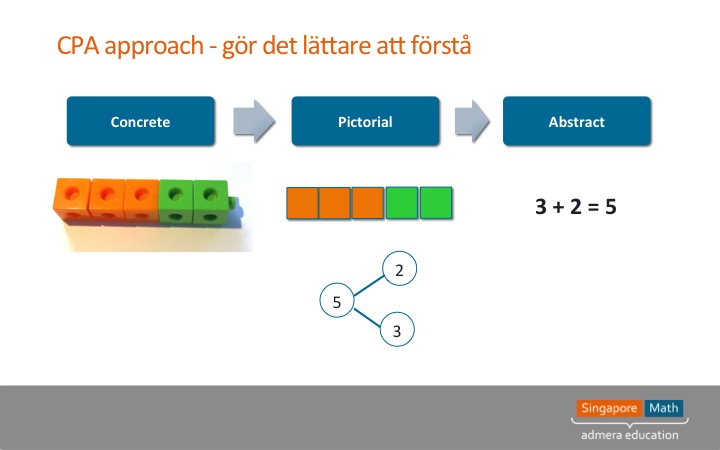
The following Grade 1 example shows how to introduce students to using tape diagrams. The use of tape diagrams supports students’ transition from concrete models to representational and symbolic models. Students can use a tape diagram to organize information and communicate their mathematical thinking.Įureka Math ® introduces tape diagrams as early as Grade 1 with addition and subtraction to reinforce the part–whole relationship. Tape diagrams are useful for solving many different types of math problems but are commonly used with word problems. A tape diagram is a pictorial model students can draw to represent a mathematical relationship or to develop understanding of a math concept.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
